Maya1 TTS Model
Open-source speech AI with expressive voice generation and rich human emotion
What is Maya1 TTS Model?
Maya1 is an open-source speech model designed for expressive voice generation with rich human emotion and precise voice design. Built by Maya Research, this model represents a significant step forward in making high-quality voice AI accessible to everyone.
This model allows you to create natural-sounding voices by simply describing them in plain language. Instead of working with complex parameters or technical settings, you describe the voice as if you were briefing a voice actor.

The model handles over 20 different emotions including laughter, crying, whispering, anger, sighing, and gasping, bringing a human touch to synthetic speech.
Maya1 runs on a single GPU and uses a 3-billion parameter architecture based on the Llama transformer model. It generates audio at 24 kHz quality and supports real-time streaming, making it suitable for production environments where low latency matters.
Maya1 at a Glance
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Model Name | Maya1 |
| Category | Text-to-Speech AI |
| Function | Emotional Voice Synthesis |
| Parameters | 3 Billion |
| License | Apache 2.0 (Open Source) |
| Audio Quality | 24 kHz, Mono |
| Hardware Requirements | Single GPU (16GB+ VRAM) |
| Streaming Support | Real-time with SNAC codec |
Supported Emotions
Maya1 supports over 20 inline emotion tags that can be embedded directly in your text for precise emotional control
<laugh><laugh_harder><sigh><chuckle><gasp><angry><excited><whisper><cry><scream><sing><snort><exhale><gulp><giggle><sarcastic><curious>Embed these emotion tags directly in your text to control emotional delivery at specific points. For example: "That's amazing
Why Maya1 is Different
Most voice AI tools today are either closed-source services that charge per second of audio generated, or open-source models that lack emotional range and natural voice control. Maya1 bridges this gap by offering production-quality emotional speech synthesis with full transparency and no usage fees.
The model stands out because it accepts natural language descriptions for voice design. You can specify age, accent, pitch, timbre, pacing, and character traits in plain English. This approach makes voice creation intuitive for developers, content creators, and researchers who need expressive speech without technical audio engineering knowledge.
Maya1 supports inline emotion tags that let you place emotional expressions exactly where they belong in your text. For example, you can insert laughter mid-sentence or add a whisper for dramatic effect. This granular control over emotional delivery creates more natural and engaging speech output.
The model uses the SNAC neural codec for audio generation, which enables real-time streaming at approximately 0.98 kilobits per second. This efficient encoding makes Maya1 practical for applications like voice assistants, interactive agents, game characters, and live content generation where latency matters.
Key Features of Maya1
Natural Language Voice Control
Describe voices the way you would brief a human voice actor. Specify age, accent, pitch, character traits, and delivery style in plain language. The model interprets these descriptions and generates matching voice output without requiring technical audio parameters or training data.
20+ Inline Emotions
Insert emotion tags directly into your text to control expressive delivery. Supported emotions include laugh, giggle, chuckle, sigh, whisper, angry, gasp, cry, and over a dozen more. Place these tags exactly where you want emotional expression to occur for natural-sounding speech.
Real-Time Streaming
Generate audio in real-time with the SNAC neural codec operating at approximately 0.98 kbps. The streaming capability makes Maya1 suitable for voice assistants, interactive AI agents, live content generation, and other applications where low latency is important.
Single GPU Deployment
Run the entire model on a single GPU with 16GB or more of VRAM. Compatible with consumer hardware like RTX 4090 as well as data center GPUs like A100 and H100. This accessibility makes Maya1 practical for individual developers and small teams.
Apache 2.0 License
Fully open-source under Apache 2.0 license. Use Maya1 commercially, modify the code, deploy in production, and build products without licensing fees or usage restrictions. Own your deployment completely.
Production-Ready Infrastructure
Includes vLLM integration for scaling, automatic prefix caching for efficiency, and WebAudio compatibility for browser playback. The architecture is designed for production deployment with features that improve performance in real-world applications.
How to Use Maya1
Getting started with Maya1 is straightforward. Follow these steps to generate your first emotional speech:
Step 1: Access the Studio
Navigate to https://www.mayaresearch.ai/studio/text-to-speech in your web browser.
Step 2: Login
Sign in to your account. If you don't have an account yet, you'll need to create one first.
Step 3: Select Text-to-Speech
In the left sidebar, select the "Text-to-Speech" option to access the voice generation interface.
Step 4: Choose Your Voice
Select a voice preset from the available options. You can choose from various voice characteristics and styles to match your needs.
Step 5: Enter Your Prompt and Emotion
Type or paste your text prompt in the input field. Select an emotion from the dropdown menu or enter custom emotion tags directly in your text using the inline emotion syntax.
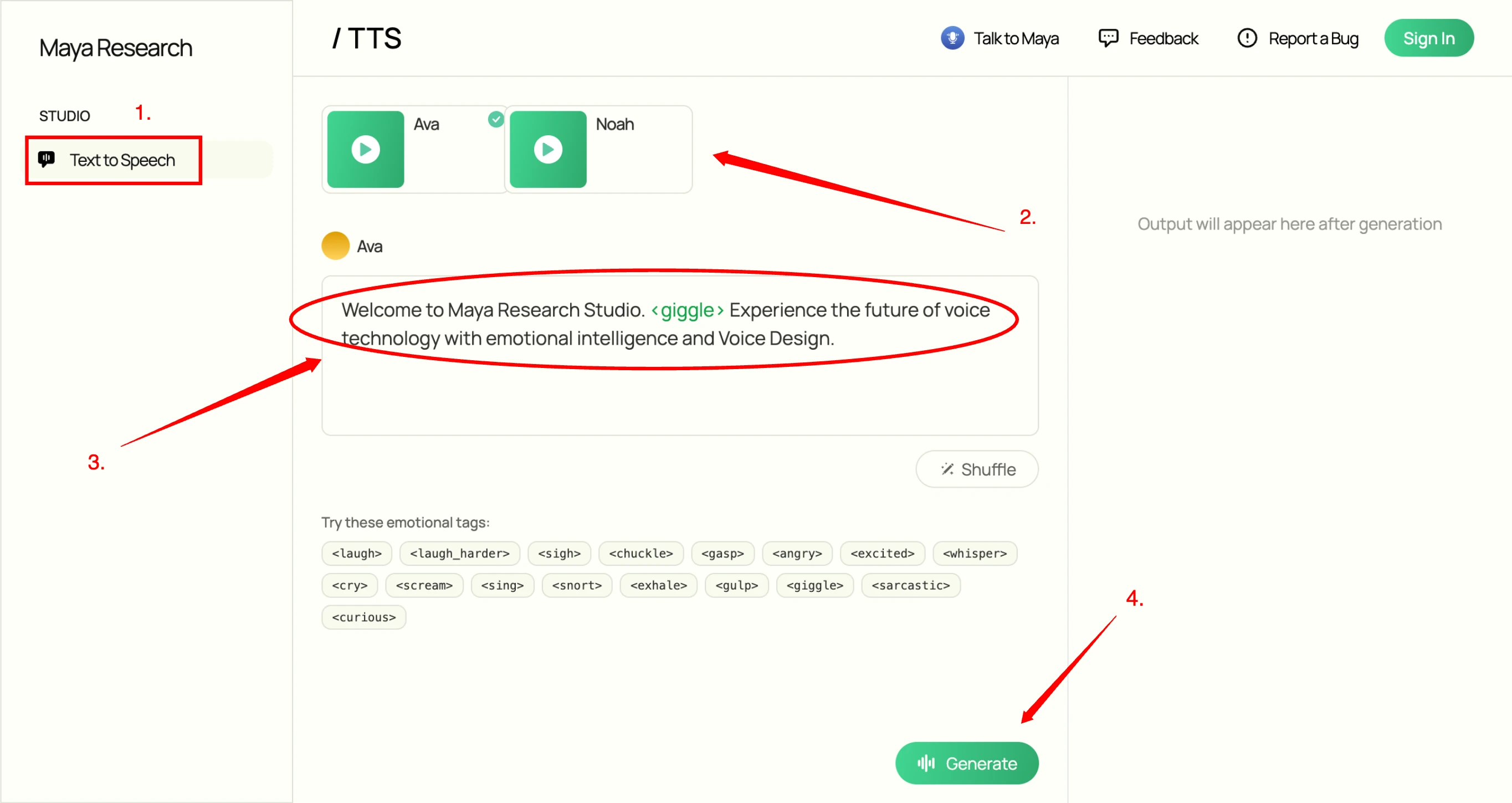
Step 6: Generate
Click the "Generate" button to create your audio. The system will process your request and produce the emotional speech output in real-time.
Technical Architecture
Maya1 uses a 3-billion parameter decoder-only transformer based on the Llama architecture. Rather than predicting raw audio waveforms, the model generates SNAC neural codec tokens. These tokens represent audio in a compressed hierarchical format that enables efficient streaming and generation.
The SNAC codec uses a multi-scale hierarchical structure operating at approximately 12, 23, and 47 Hz. This structure keeps autoregressive sequences compact while maintaining audio quality. Each audio frame requires 7 tokens, making the generation process efficient enough for real-time applications.
The model was pretrained on an internet-scale English speech corpus to learn broad acoustic patterns and natural coarticulation. After pretraining, supervised fine-tuning used a curated dataset of studio recordings with human-verified voice descriptions, over 20 emotion tags per sample, multi-accent English coverage, and character variations.
The training pipeline includes 24 kHz mono resampling with loudness normalization, voice activity detection for silence trimming, forced alignment for clean phrase boundaries, text deduplication using MinHash-LSH, audio deduplication with Chromaprint, and SNAC encoding with 7-token frame packing.
Installation and Setup
Getting started with Maya1 requires installing a few Python packages and loading the model from the Hugging Face model hub. The process takes just a few minutes on a system with the appropriate GPU.
Requirements
Install the necessary Python packages:
pip install torch transformers snac soundfile
Loading the Model
You can load Maya1 directly from Hugging Face or clone the repository:
# Load directly in Python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"maya-research/maya1",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("maya-research/maya1")Quick Start Example
Generate your first emotional speech with this example:
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from snac import SNAC
import soundfile as sf
# Load models
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"maya-research/maya1",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("maya-research/maya1")
snac_model = SNAC.from_pretrained("hubertsiuzdak/snac_24khz").eval().to("cuda")
# Design your voice
description = "Realistic male voice in the 30s age with american accent. Normal pitch, warm timbre, conversational pacing."
text = "Hello! This is Maya1 <laugh> the best open source voice AI model with emotions."
# Generate speech
prompt = f'<description="{description}"> {text}'
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
with torch.inference_mode():
outputs = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=500,
temperature=0.4,
top_p=0.9,
do_sample=True
)
# Process SNAC tokens
generated_ids = outputs[0, inputs['input_ids'].shape[1]:]
snac_tokens = [t.item() for t in generated_ids if 128266 <= t <= 156937]
# Decode to audio
frames = len(snac_tokens) // 7
codes = [[], [], []]
for i in range(frames):
s = snac_tokens[i*7:(i+1)*7]
codes[0].append((s[0]-128266) % 4096)
codes[1].extend([(s[1]-128266) % 4096, (s[4]-128266) % 4096])
codes[2].extend([(s[2]-128266) % 4096, (s[3]-128266) % 4096, (s[5]-128266) % 4096, (s[6]-128266) % 4096])
codes_tensor = [torch.tensor(c, dtype=torch.long, device="cuda").unsqueeze(0) for c in codes]
with torch.inference_mode():
audio = snac_model.decoder(snac_model.quantizer.from_codes(codes_tensor))[0, 0].cpu().numpy()
# Save output
sf.write("output.wav", audio, 24000)
print("Voice generated successfully! Play output.wav")What You Can Build
🎮 Interactive Characters
Generate dynamic dialogue for game NPCs with real emotions that match the story.
📚 Audio Content
Narrate audiobooks and podcasts with consistent voices and natural emotional delivery.
🤖 Smart Assistants
Create voice bots that respond with appropriate emotions in real-time conversations.
🎬 Video Voiceovers
Add expressive narration to educational videos, tutorials, and social media content.
♿ Accessibility Tools
Build engaging screen readers with natural voices for extended listening.
💬 Customer Support
Deploy empathetic voice bots that improve automated customer service experiences.
How Maya1 Compares
| Feature | Maya1 | Others |
|---|---|---|
| Open Source | Yes | Mostly No |
| Emotions | 20+ | Limited or None |
| Voice Design | Natural Language | Complex Setup |
| Cost | Free | Pay-per-use |
| Customization | Full Control | Limited |